www.iab.com/newadportfolio
#IABNewAdPortfolio
© 2017 IAB Technology Laboratory
1
Fixed Size Ad Specifications
The following fixed size ad units are recommended as part of the new ad portfolio. These have been recommended
based on Attitudes and Usage Study to determine which of the ad units, contribute to the majority of revenue and are
sufficient to advertise across multiple screen sizes.
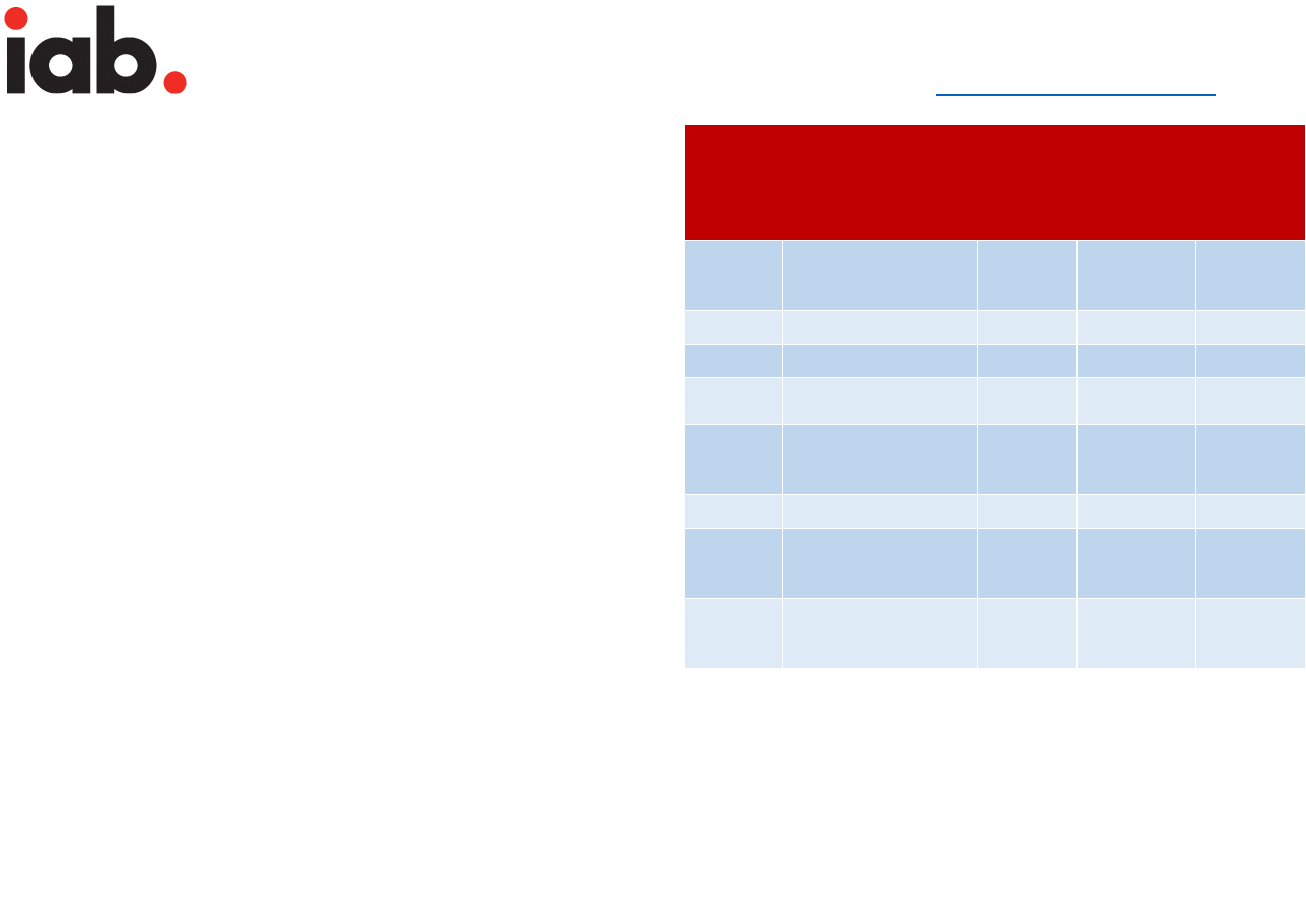
Ad unit Name
Fixed Size (px)*
Max. K-Weight (kB)
Initial Load
Subload
Billboard
970x250
250
500
Smartphone Banner
300x50 or 320x50
50
100
Leaderboard
728x90
150
300
Super Leaderboard/ Pushdown
970x90
200
400
Portrait
300x1050
250
500
Skyscraper
160x600
150
300
Medium Rectangle
300x250
150
300
20x60
120x60
50
100
Mobile Phone Interstitial
640x1136 or 750x1334 or 1080x1920
300
600
Feature Phone Small Banner
120x20
5
N/A
Feature Phone Medium Banner
168x28
5
N/A
Feature Phone Large Banner
216x36
5
N/A

www.iab.com/newadportfolio
#IABNewAdPortfolio
© 2017 IAB Technology Laboratory
2
General Ad Requirements (apply to all
ads)
• Interest-Based Advertising (IBA): Include IBA self-
regulation controls for ads using behavioral targeting (5kB
max file size).
• Audio: Audio in ads should be muted. To allow for audio
initiation in ads, a control may be included for the user to
initiate audio. See the LEAN user experience and ad
content guidance for more on audio in ads.
• Defining ad space: Ad unit content must be clearly
distinguishable from publisher or unpaid content on the
page (for example an ad unit may have clearly defined
borders so it is not confused with normal page content).
• CPU Load: Ads should be developed to perform
smoothly and not interfere with site or app performance.
30% CPU load max (based on the average CPU of the
user base) per active ad. Please review the LEAN
guidance for more details on CPU load.
• Maximum number of host-initiated file requests: Ad
must not exceed ten file requests during initial file load.
Additional files can be loaded as necessary during host
initiated subload and user initiated loads.
General Notes
• Initial file load: Includes all assets and files necessary
for completing first visual display of the ad and requested
before load event dispatched by the window object.
• Host-initiated subload (subload): This is the
additional file weight an ad can load in addition to initial
load. Ad file subload may begin after the load event has
been dispatched by the window object. The ad should
listen for the load event dispatched by the window object
of the host page. When communication with the host page
is not possible, then it is acceptable to listen for the load
event dispatched by the window object of the ad iframe.
• File weight calculation: For calculating ad file weight,
all files for the ad, including those shared libraries not
exempt by the publisher or ad server, must be included as
part of the maximum file weight calculation. File weights
are calculated after files have been compressed into gzip
format.
Initial Load K-Weight= All ad files + Non-exempt
shared libraries + max 50 kB for all exempt Shared
Libraries
Subload K-Weight = All ad files + all non-exempt
shared libraries
See the LEAN user experience and load performance guidance for
details on initial load, subload, and shared libraries
www.iab.com/newadportfolio
#IABNewAdPortfolio
© 2017 IAB Technology Laboratory
3
• User-initiated file size: Unlimited file size load is
allowed after user-initiated interaction. Ad should be
responsible for bandwidth and device capabilities while
doing so. User initiation is the willful act of a user to engage
with an ad. User interaction is the discrete user action with
the ad or its elements, e.g. click or tap or other complete
and discrete gesture.
• Static file weight and static image size: Use Initial
Max K-Weight guidance for static image only ads or
backup file requirements.
• Slow internet connection: For 3G (1.5 Mbps
download speeds) or slower connections, the file weights
should be 30% less than recommended.
File sizes in this specification are defined for the creative assets and
files required for creative rendering and management of the ad. Ad
server files or other non-creative services files like measurement or
verification must not be counted against ad K-weight.
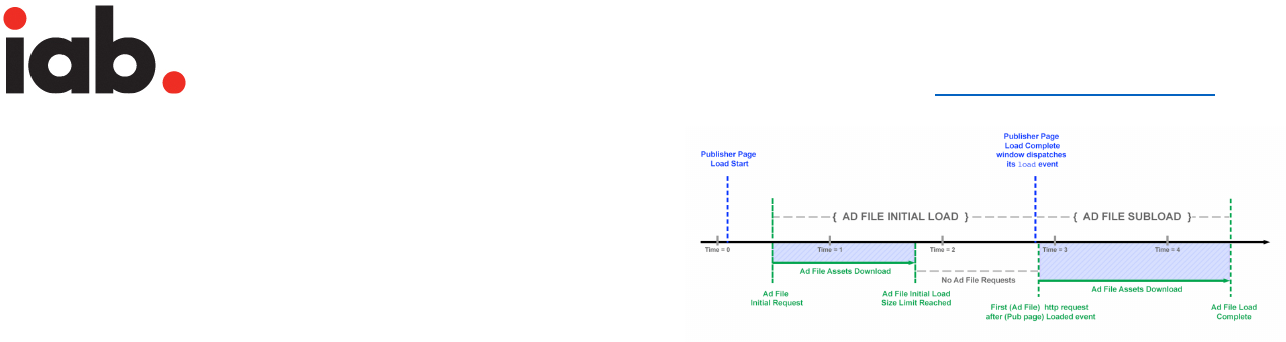
Flexible Ad Sizing Grid
The sizing grid is a LEAN standard based range of k-
weights for an ad of given pixel size. This will allow self-
determination of ad specification for innovative and
custom ad formats that may not be part of IAB Ad Portfolio.
Size
Group
(x1000
pixels)
Example of
Previous IAB
Fixed Sizes
Max
Initial
K-
weight
(kB)
Max
subload
K-weight
(kB)
Static
Image
(e.g. .jpg
.png or
.gif) kB
Less
than
180
320x50, 300x50
50
100
50
120-180
N/A
75
150
75
180-300
728x90
100
200
100
300 -
500
970x90,
160x600,300x250
150
300
150
500-700
Full Page (Small
Phones <4.5"
screen)
200
400
200
700-900
300x600, 970x250
250
500
250
700-1m
Full Page (Large
phones > 4.5"
screen)
300
600
300
1m +
Full page (Large
devices > 7 "
screen)
350
700
350
Sizes for fixed size ad units are calculated based on double density
(or 2x) resolution.
E.g. 728x90 size will be 728*90*4= 262080 pixels.
For flexible size ad units, the sizes are calculated using midpoint of
the size height and width at 2x resolution. E.g. 8:1 ad unit
recommended size is 900*112.5*4 pixels which is in the 300k- 500k
pixel range.
Transition fixed size ad units in the flexible size specification grid will
follow the size determined by the corresponding aspect ratio ad unit
www.iab.com/newadportfolio
#IABNewAdPortfolio
© 2017 IAB Technology Laboratory
4
LEAN: User Experience and Load
Performance
The new guidance creates a positive user experience of
advertising by way of maximizing page load performance.
The ad must:
1. Use light weight file loads during initial load of the page
2. Eliminate or minimize render blocking scripts like CSS,
JavaScripts during initial load
3. Use subload for rendering ad experiences that require
heavy file weights
4. Minimize number of files requested during initial load
5. Make user initiation required for ad functionality that
needs large file downloads
Initial vs. Subload vs. User Initiated Load
For the purpose of defining initial load and subload, the
load event dispatched by the publisher page’s window
object is considered as the event to separate the initial
load from the subload of the ad content. Subload must not
start prior to this load event is dispatched. When an ad is
nested in an iframe that does not allow the ad document
to capture the load event of the publisher page, then it can
use the load event of the ad document’s iframe.
Initial Load is defined as all files requested by the ad to
render the creative when the page starts loading. It
includes all files sent by the ad server to the page (image,
HTML5, JS, CSS, Sprite sheets, Video files) and any other
files requested by the ad for creative rendering and
management before the load event is dispatched by the
window object.
Subload is defined as all files requested by the ad after
the load event is dispatched by the window object. It
includes all files requested by the ad (auto initiated without
any user interaction) to the page (image, HTML5, JS, CSS,
Sprite sheets, Video files) for the purpose of creative
rendering and management.
Subload must start after the load event has been
dispatched by the window object of the page or the ad
iframe.
User Initiated Load is the file weight of all assets loaded
when a user initiates interaction with the ad. Unlimited
gzipped file load is allowed for any creative assets loaded
after user-initiated ad interaction, like expansion or clicks.

www.iab.com/newadportfolio
#IABNewAdPortfolio
© 2017 IAB Technology Laboratory
5
While no limit has been placed on user initiated load, ad
developers should consider user experience and load
performance as part of their ad design.
The assets for user initiated ads should be optimized for
load performance, and only necessary assets should be
loaded.
File Requests
The maximum number of Initial Load file requests
allowed is 10.
HTML5 ads are like mini web pages and the number of
requests made to fetch files has a big impact on load
performance of the ad as well as on the page.
This file request limit only applies to the initial load. No file
request limit has been placed on subsequent file loads.
HTTP2 standard allows multiple requests per connection.
This will negate the need for this standard in the future
when HTTP2 adoption is at acceptable levels. Currently,
most browsers support it
(http://caniuse.com/#search=http2), but content and ad
server adoption is low at ~10%. More information on
HTTP2 is available here: https://http2.github.io/faq/. And
more data on adoption is available here:
https://w3techs.com/technologies/details/ce-http2/all/all
Managing CPU Load
High CPU load generated by uninitiated functions should
be minimized. CPU load generated by animation should
stop once animation is complete. Higher CPU load is
allowed for user-initiated functions (animation,
interactivity, etc.) as long as the page or app continues to
function smoothly.
Poor performance of an ad in an isolated instance can
indicate that it will negatively affect performance of a site
or app when the ad is loaded into a live environment.
Optimize those features that generate high CPU load. For
example, if high CPU load is exhibited during animation,
try to optimize animation by reducing the number of
elements animated at one time.
Avoid using setTimeout and setInterval in
animation scripts, etc. Animation scripts should not be
executed when the ad is not in view.
In-page banners must delay initiating animation until the
load event is dispatched by the window object
What is gzip?
All assets for HTML5 ads must be packaged together for
delivery. To optimize the file size for delivery to a browser,
all assets should be delivered in compressed format. The
common method for compressing files in transition over
the Internet is the gzip utility, which is free to use and
supported by all modern browsers. Ad servers compress
ad files they serve as part of their general process.
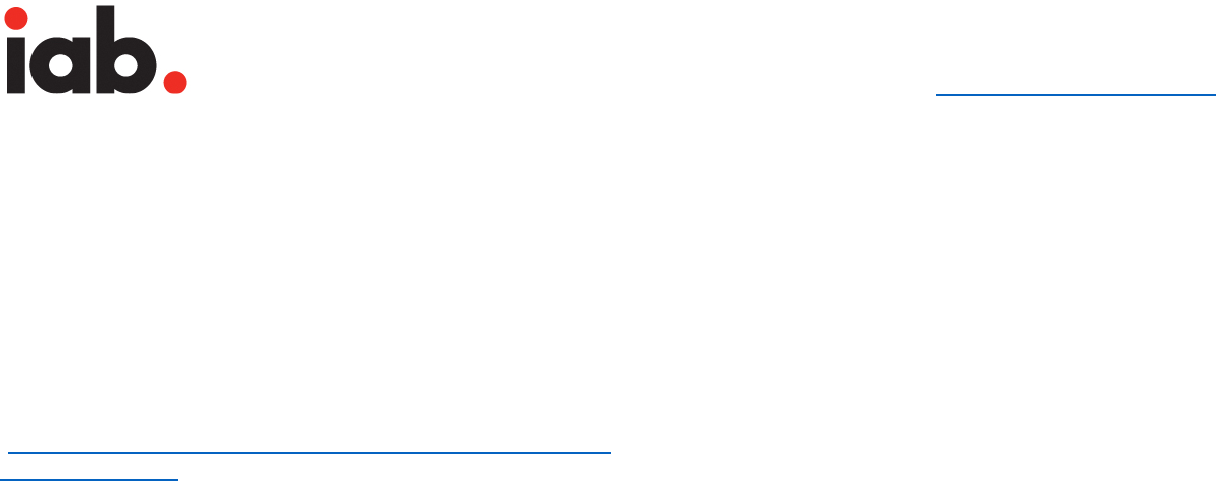
www.iab.com/newadportfolio
#IABNewAdPortfolio
© 2017 IAB Technology Laboratory
6
Shared Libraries and Resources
Browser caching capabilities benefit all parties by
eliminating the need to download previously requested
resources that already exist on the user’s device.
Advertisers (Creative developers) are encouraged to
take advantage of browser caching functionality by linking
to shared libraries hosted on the Ad Serving party’s
(Publisher ad server or third-party ad server) domain that
are used across campaigns.
Please refer to the IAB HTML5 Resources wiki
(https://wiki.iab.com/index.php/HTML5_for_Digital_Advert
ising_Resources) for commonly used shared libraries and
check with the ad serving party for the ones that are
hosted.
Publishers and first-party ad servers should specify the
shared library name(s) and originating CDN url(s) that are
exempt and can be excluded from file weight calculations
in their ad specifications and guidance to advertisers. They
must provide reasonable notice for the advertiser to
update creative.
Shared libraries that are exempt are allowed a combined
maximum of 50 kB file weight (gzipped) as part of initial
load. No limit is imposed during subload. Any shared
library and CDN NOT specified in publisher or ad server
guidance must be counted in file weight calculations
submitted by advertisers.
Other shared resources for which the publishers
and ad servers are encouraged to take advantage
of browser caching functionality are Web Fonts, DAA
provided AdChoices insertion, and CSS packages
Render Blocking Elements
JavaScript is a render blocking script that blocks the DOM
construction and delays page content rendering.
It is recommended that all JavaScript be executed as
asynchronous and executed inside a sandboxed i-frame.
CSS also blocks rendering. Styles to HTML5 elements can
be implemented in three ways:
1. External CSS: These are CSS files external to the ad
HTML and are referred to by the ad when it wants to
apply a style.
2. Internal CSS: These are CSS definitions that are inside
the ad HTML document
3. Inline Style: In this method, the ad does not call a CSS
element from another file, but each element has its
style defined in the element definition itself
Inline style method is the most efficient of the above
methods and it is recommended to use inline style method
to minimize load time. Embedded styles may also be used.
Since ads are usually not multi-page websites, using
external CSS for ads does not offer the typical advantages
of external CSS and may add file weight and number of
files to the ad load.
